Addisons Disease Causes Diagnosis and Treatment
Addisons Disease – a condition characterized by cortisol deficiency (cortisol, a hormone secreted in the adrenal cortex), commonly resulting from an underlying adrenal failure (primary adrenal insufficiency).
Causes of hypocortisol
Decreased cortisol secretion can result from the following:
Primary adrenal insufficiency ( adrenal failure, decreased serum Na, increased serum K, Ca) a condition at which the adrenals are not capable to produce enough cortisol
Secondary adrenal insufficiency a condition related to a problem in the signal the brain sends (through ACTH) to the adrenals instructing them to secrete more cortisol, the adrenals in this case also fail to produce enough aldosterone.
Symptoms
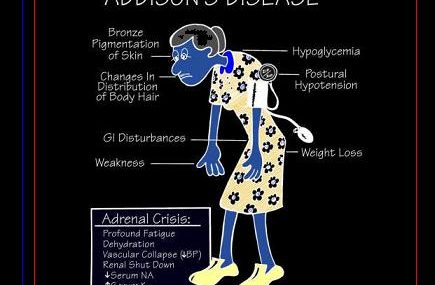
Main symptoms of addisons disease include weakness, fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, weight loss, low blood pressure, darkened skin, salt craving, dizziness upon standing, depression
Blood analysis shows high serum potassium, low serum sodium
Causes of Hypocortisolemia
1- Primary adrenal insufficiency.
2- Secondary adrenal insufficiency, it is caused by a chronic use of steroids
3- An injury in the hypothalamus that leads into a decreased secretion of corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH), which results in a decreased secretion of ACTH and lastly resulting in a decreased amount of cortisol.
4- Autoimmune poly-endocrine syndrome APS1 (childhood) and APS2 (17-32)
5- Amyloidosis a process at which protein builds-up in organs replacing functional cells
6- Various causes such as adrenal metastases (cancer spread to the adrenals), infections, bleeding into the adrenals
Diagnosis and Testing
Baseline laboratory tests for cortisol and Acth in blood
1- Acth stimulation test, to diagnose primary adrenal insufficiency , at which the physician draw blood measure cortisol and Acth after that he inject cosyntropin then draw blood again after 30-60 minutes to check cortisol and Acth (normal response reflects an increase in cortisol level)
2- Insulin tolerance test, it is used to diagnose primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency and is considered a golden standard (contradicted in ischemic heart patients and patients suffering of epilepsy)
Test
We inject insulin to decrease blood glucose, decreased blood glucose will stimulate the pituitary to secrete more Acth (normal response reflects an increase in cortisol level)
Other normal responses include sweating, rapid heart rate and hunger
* We draw blood periodically and measure cortisol as glucose level drops.
3- CRH stimulation test, (a) we inject CRH that will stimulate (b) the pituitary to secrete Acth that will stimulate (c) the adrenals to secrete cortisol; the test reads as the following:
If (b) not (c) then its addison disease
If no (b) then its secondary adrenal insuffieciency
If delayed (b) then its problems in the hypothalamus
4- Imaging tests, CT of the abdomen & MRI of the brain.
Treatment
Treatment starts by treating the cause behind hypo-cortisol, then the patients are prescribed cortisone (IV or PO), to control and release the symptoms of cortisol deficiency.
All medicament’s should be prescribed and administered under the supervision of a doctor.
2- Diet Number 2, that excludes all types of salts from the table, excluding animal fats and reducing the allowable amounts of additive sugar and sweets a person can eat on daily basis, sugars and carbohydrates should not compose more than 15% of the daily caloric needs.
All About Addisons Disease Causes Diagnosis and Treatment
Verified by: Dr.Diab (January 7, 2017)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (January 7, 2017). Addisons Disease Causes Diagnosis and Treatment. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 5(2). urn:medcoi:article4158.














There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks