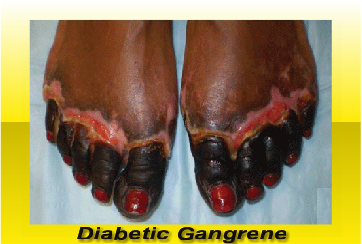
Diabetic Gangrene – a side effect of Peripheral Neuropathy
Overview
Diabetes is a disease characterized by the inability of the human body to control the level of blood sugar leading to a compromised immune system, as hyperglycemia or excessive amounts of sugar in blood damages not only the blood vessels, but also damages the nerves. This damage of nerves is known as peripheral neuropathy.
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy alters pain sensation and compromises the ability to feel any pain at the peripheries. So, a diabetic person will not feel pain neither he will notice if he is having a micro injury or cut, and because diabetes alters the immune response and reduces blood flow to the periphery, an infection may occur in the injured tissue, which may lead to gangrene by reducing perfusion pressure to its minimum and causing poor cellular perfusion (decreased tissue perfusion, cellular hypoxia, and poor end-organ perfusion).[1][2]
Symptoms
The following symptoms are indicative of a Diabetic gangrene, knowing them may help you in recognizing it
- Discoloration of skin – depending on the type of gangrene your skin may convert into red, bronze, black, purple or blue.
- Numb feeling due to severe pain.
- A foul smelling discharge coming out from the injured area.
If gangrene is affecting the epidermis and the tissues under the skin, then it may be internal or gas gangrene, it is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Pain and swelling in the tissues
- A generalized feeling of being unwell due to fever, which may lead into sepsis and death
Diagnosis
Diabetic gangrene is diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history and by the following tests
- Blood tests – acute leukocytosis, a sudden increase in WBCs may be a sign of infection
- Imaging tests – MRI, CT scan and X-rays are helpful to analyze the gangrenous necrosis inside the body.
- Arteriogram test may be conducted to get the insight of your arteries. In this test a dye is injected to the blood and with the help of X-ray the flow of blood is determined inside the arteries. With the help of this test any blockage in the arteries can be diagnosed.[3][4]
- Surgery – To know the extent of gangrene surgery can also be performed.
Treatment
Once gangrenous necrosis is triggered, permanent damage indicating irreversible cell injury occurs, as permanent organ damage occurs after normothermic ischemia of 30 min or even less in the presence of other factors such as is the case of a diabetic infection.[5][2]
Treatment for Diabetic gangrene involves debridement of the dead, damaged, or infected tissue and treating the nearby tissue at risk, to prevent the spread of infection and to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue.
After first aid is accomplished and condition is stabilized, treating the underlying condition that caused gangrene is a high priority.
Common treatments to prevent the progression of Diabetic gangrene include:
- Surgery – “Amputation of the affected part” With the help of surgery, damaged tissue can be removed to prevent further infection. It improves the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Diseased or damaged blood vessels near the infected area can be repaired with the help of surgery. Skin grafting is also an effective treatment for gangrene. Healthy skin is taken from some other part of the body and implanted over in a way to cover the infected area with the help of skin grafting technique.
- Antibiotics – Antibiotics are often used to treat gangrene or gangrenous infection.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy – this therapy is used to treat gas gangrene, as breathing 100% oxygen while under increased atmospheric pressure the wounds heal faster.[6][7]
Prognosis
Diabetic patients have a need for care or support, to aid them and keep them safe from injuries and gangrene. Some of the preventive measures are listed below:
- To control and regularly monitor the blood sugar level on daily basis, to keep it within the normal boundaries.
- Routine foot care – Being a diabetic patient you should take care and always inspect your foot for cuts or injuries. You may not feel it, but it is important to check your foot everyday to avoid infections and lower the risk of developing gangrene.[8][9][10]
References
- surgicalcriticalcare.net/Lectures/shock_overview.pdf
- emc.healthyorthodoxmedicine.com
- nhs.uk/Conditions/Gangrene/Pages/Diagnosis.aspx
- nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/007218.htm
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3904795/
- fda.gov/ForConsumers/ConsumerUpdates/ucm364687.htm
- uhms.org/resources/hbo-indications.html
- nhs.uk/Conditions/Gangrene/Pages/Prevention.aspx
- wikihow.com/Prevent-Gangrene
- cdc.gov/diabetes/ndep/pdfs/ppod-guide-podiatrists.pdf
Diabetic Gangrene
Verified by: Dr.Diab (January 7, 2017)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (January 7, 2017). Diabetic gangrene Symptoms and Treatment. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 10(2). urn:medcoi:article2729.














There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks