Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Definition
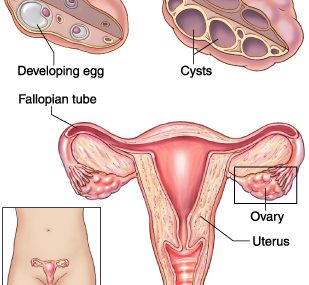
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a benign disorder typically beginning around the onset of puberty and worsening through the late pubertal years, it is characterized by irregular menses, mild obesity, hirsutism and less commonly amenorrhea. Upon examination, most patients have abundant cervical mucus and elevated free estrogens and androgens.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is the most common cause of oligomenorrhoea (infrequent periods) and amenorrhoea (absence of periods), it affects about 4-8 percent of women globally.
Symptoms
What are the main symptoms of PCOS?
- Irregular periods, prolonged menstrual bleeding that goes beyond a month (2-3 months)
- Infertility or an inability to conceive after having regular unprotected sex for more than a year
- Abdominal mass (adnexal mass)
- Weakness
- Emotional liability and depression
- Pain during sex (dyspareunia) and dry vagina (atrophic vaginitis)
- Hirsutism or excessive male-pattern hair growth (extra facial and body hair)
- Acne
- An alteration in taste and a decrease in the ability to taste food (dysgeusia and hypogeusia)
- Loss of Appetite (low appetite)
- Excessive Sweating and mild obesity
- High levels of insulin
Causes
What is the cause of polycystic ovary syndrome?
PCOS is caused by hormonal imbalance due to impaired hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis (HPO axis) function. PCOS usually occurs when LH or insulin levels are too high, which then stimulates the ovaries to make extra amounts of testosterone.
Hyperandrogenic chronic anovulation is a benign disorder caused mainly by a genetic or endocrine pathology in which the ovaries start making slightly more androgens. Higher than normal androgen levels can prevent the ovaries from ovulation during a monthly menstrual cycle. Normally, ovulation occurs once in every menstrual cycle when hormone changes stimulate your ovaries to release an egg. Moreover, higher than normal androgen levels can also lead to high levels of insulin and can cause extra hair growth and acne.
Treatment
How to treat polycystic ovary syndrome?
- Classical treatment:
Laparoscopic resection of the ovaries (after diagnostic confirmation)
Metformin is an ovulation induction agent used for anovulatory infertility in women with PCOS
Clomiphene (clomifene, clomiphene citrate) is a drug used to treat infertility (to cause ovulation) in women with PCOS who do not ovulate. Clomiphene stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete an increased amount of FSH and LH. This in turn stimulates the growth of the ovarian follicle and thus initiates ovulation. Clomiphene is taken by mouth once a day. Use increases the chance of twins. Alternatively, aromatase inhibitors (AIs), such as letrozole (femara) are often used alone or with other medical therapies for ovulation induction in PCOS patients (patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome).
The use of Metformin in combination with Clomiphene Citrate for ovulation induction have been shown to improve ovulation and pregnancy rates in clomiphene-resistant infertile patients with polycystic ovarian disease (PCOS). However, the efficacy of metformin and clomiphene citrate combination for ovulation induction in infertile patients with PCOS was not found to be superior to monotherapy with either clomiphene or metformin
Dexamethasone 0.25 mg daily for six months reduces androgen levels in women with PCOS who were treated with Metformin and who are overweight.
Next steps management
How to diagnose pcos?
Your doctor manually inspects your reproductive organs for masses or other anatomic abnormalities
How to test for polycystic ovary syndrome?
Diagnostic tests include:
- Dexamethasone suppression test
- ACTH stimulation test
- Blood tests to check the levels of three important levels: FSH (follicle stimulating hormone), LH (luteinizing hormone) and estradiol (E2). Normal LH and FSH levels usually range between 5 and 20 mlU/ml serum.
- Pelvic ultrasound to detect abnormalities affecting the ovaries and uterus and to evaluate the uterus, cervix, ovaries, fallopian tubes and bladder. In women with pcos, ovaries usually contain 2- 6 mm follicular cysts and may be enlarged with smooth, thickened capsules. However, ovaries may be normal in size as well
- Diagnostic laparoscopy
References
Verified by: Dr.Diab (December 18, 2017)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (December 18, 2017). Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 4(2). urn:medcoi:article15595.













There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks