Scrub Typhus Once a Killer Disease is Now down with Modern Treatment
Definition
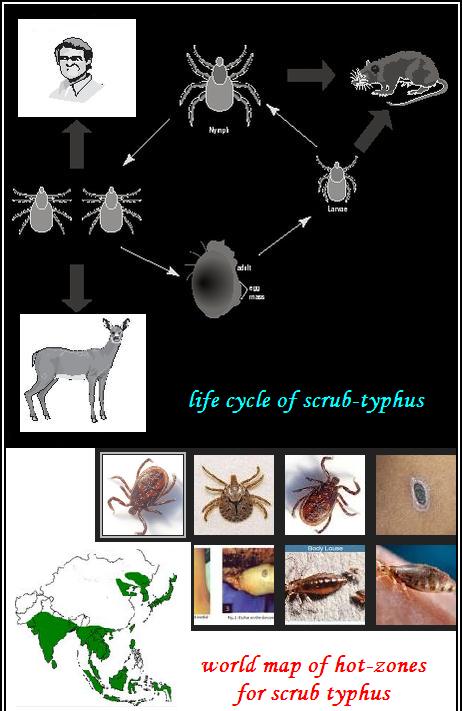
Scrub Typhus (bush typhus) is an acute mite-borne and transmittable infectious disease caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi, a gram negative bacteria commonly found in trombiculid mites. The name scrub typhus was derived from the type of terrain that harbors this insect.
How do you get scrub typhus?
You may get involved with scrub typhus while traveling to a place where scrub typhus is endemic.
How is scrub typhus transmitted to humans?
Scrub typhus is a mite-borne disease transmitted by the bite of trombiculid mite larvae (chiggers), which feed on rural rodents, such as voles, rats, and field mice.
You may not notice or feel any pain from the chigger bite but it is enough for you to get infected.
What is the incubation period for scrub typhus?
The incubation period of scrub typhus ranges from 6 to 20 days.
Symptoms of scrub typhus
What are the symptoms of scrub typhus?
Common symptoms of scrub typhus include:
- Headache
- Shaking Chills
- Lymphadenopathy
- Conjunctival injection
- Fever
- Anorexia
- General Apathy
Besides, painless small rashes with necrotic centers may also appear, rash increasing by size, which may form scars following the healing process.
Along with fever if you notice rashes and sores or bumps then it is a strong sign of scrub typhus, which needs an immediate treatment.
A chigger bite is painless and remains unnoticed until it forms a scar, which is followed by high fever in most cases.
Other non frequent signs indicating scrub typhus include:
- Ocular pain accompanied with wet breathless cough and malaise. The person may develop pneumonia if untreated.
Diagnosis of scrub typhus
How to confirm a diagnosis of scrub typhus?
Lab tests of patients with scrub typhus usually show the following:
- Hypoalbuminemia
- Elevated transaminase levels
- Haematological manifestations of scrub typhus, which can be confused with dengue infection
- Thrombocytopenia
- Decreased cd4/cd8 ratio
- Late lymphocytosis with early lymphopenia
How to diagnose scrub typhus?
Common diagnostic tests include: skin biopsy, western blot test, and serologic tests for antibodies, such as indirect fluorescent antibody test, and rapid diagnostic reagent for scrub typhus.
Optional tests include:
- Weil-Felix agglutination test to detect Scrub Typhus agglutinate OXK strain
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay
- Rapid immunochromatographic tests for detection of IgM and IgG
- A rapid dot immunoassay (dot-enzyme-immunoassay test) for the detection of serum antibodies
- Indirect immunoperoxidase assay (IPA)
- X-ray of the chest to detect pneumonia
- A complete blood count (CBC)
Treatment of scrub typhus
How to treat scrub typhus and what antibiotics are used to treat scrub typhus?
To treat Scrub typhus, your doctor may prescribe one of the following medications:
Antibiotics, such as chloramphenicol, macrolides, and tetracyclines (doxycycline). If antibiotics are not administered properly, the disease may reoccur. If the patient is not in condition to take pills, intravenous (IV) administration of antibacterial agents must be initiated.
Doxycycline, a tetracycline, is a popular variant often used to treat both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial infections.
To note, HIV decreased the severity of scrub typhus, as the immune system of HIV patients shows a powerful response towards the antigen.
Patients with scrub typhus are encouraged to avoid all kinds of outdoor activities and extreme unhealthy diets. Moreover, patients suffering from severe scrub typhus may need inpatient care to avoid circulatory collapse.
A requirement for meticulous supportive care is usually needed.
Prognosis
Prognosis may vary from one patient to another depending on the severity of the disease, age and health status of the patient. For scrub typhus, no prognosis has been established. However, strain heterogeneity and incomplete immunity often leads to reinfection.
The mortality of untreated patients ranges from 1 to 60%, which is affected by factors such as age, region and strain. However, with the availability and effectivity of antibiotics, death due to scrub typhus is rare, but with improper therapy the recovery process can be accompanied with complications. Nowadays, therapeutic novels has reduced the recovery time for most patients, but 15% of the deaths are due to delayed or misdiagnosis, for an example mortality rate increases in case a scrub typhus patient has been caught by acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Scrub Typhus
Verified by: Dr.Diab (September 16, 2018)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (September 16, 2018). Scrub Typhus Definition Symptoms and Treatment. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 21(2). urn:medcoi:article1150.














There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks