How to Relieve Sciatica when Pregnant
1- Understanding sciatica
Sciatica a progressive form of Radiculopathy arising mainly from a local entrapment, compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve that conducts motor impulses from the central nervous system (CNS) to the terminal nerves of the legs or periphery (target cells), and sensory impulses from the peripheral nerves to the central nervous system, leading to the lumbosacral radicular syndrome (the feeling of weakness, pins, or pain) with a bunch of other symptoms related to the lower back and legs.
Sciatic nerve plays two major roles:
- Sensory function – allowing us to feel sensations in our legs and lower back
- Motor function – voluntary control over our muscles, allowing us to move, and organize the muscles in our legs/feet granting us the ability to sit, stand, walk, etc…
Pathogenesis
The leading causes of nerve entrapment or compression include:
- Degenerative disc disease (Injured disc, the degeneration of at least one of the inter-vertebral discs of the lumbosacral part of the spinal cord)
- Spondylolisthesis (slipped disc, a post-fracture forward displacement of a disc, especially the fifth lumbar vertebra)
- Pressure on the sciatic nerve caused by Inflammation of the nearby tissue or organs
- Pressure on the sciatic nerve caused by a growing nearby tumor
- Lumbar spinal stenosis (the narrowing of the spinal canal in the lower back mostly due to age related changes and diseases such the degenerative arthritis of the spine)
- A trauma resulting in bruises and/ or bone fractures
- Pregnancy
Compression of the sciatic nerve is very unpleasant, and usually results in extreme pain. The diagnosis of sciatica in most females is set on the onset of chronic progressive malaise that seems to acquire the annoying feelings of pins and needles hitting them deep in their legs. As a rule sciatic complains, arise or show up in the course of and/or following a hard work. It is known that sciatic symptoms are progressive in nature and thus sciatic pain arising from a disc or compression increases and worsens over time until it reaches a moment that the affected females cannot tolerate the amount of pain, and at this particular moment, most females refer to nearby clinics or doctors for consultancy and help.
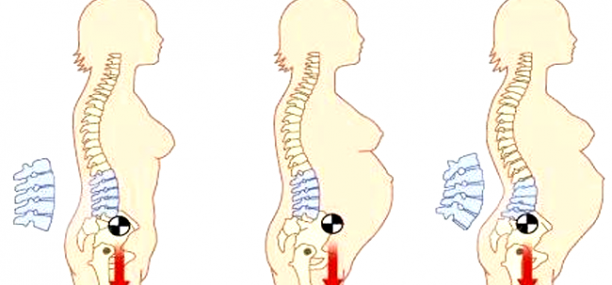
In pregnant women, sciatica as a disease often arises of disc damage irritated by pregnancy that for a reason or another builds on the existing pathology to cause the swelling or inflammation around the nerve, but the growth of the baby in itself is not the direct causative reason.
Symptoms in pregnant women
- Ongoing chronic pain affecting the buttock and leg
- Shooting pain with the sensation of burning tingles commonly affecting one extremity example one leg or one foot
- Pain that shows abruptly (especially when sitting), and relieves spontaneously.
- Scrolling irradiating pain in the lower back, starting at the dorsal side of the upper thigh and scrolling down along the dorsal side of the leg to reach the foot
- Tingling sensation and numbness in the feet
- The feeling of needles in your leg or feet
- Weakness or numbness leading to difficulty moving the leg or standing on the foot
- The pain may be extreme, intense and widespread to a level that females cannot behold without sedatives and painkillers, seek help and call 911 immediately if you feel any symptoms of progressive, and weakness in your lower extremities with or without the loss of bladder or bowel control.
Diagnosis
Clinical interview
Collecting the history disease is a mandatory step in ruling out Sciatica, especially in pregnant women, gynecologists prefer asking questions to rule out any possible underlying conditions such as Osteoporosis, various infectious diseases and in particular tuberculosis (a main cause of osteomyelitis), arthritis, paget’s disease of bone, spinal stenosis, infectious immune disease such as HIV, blood cancers, etc…
Manual testing
As a rule, it is the next step after collecting the history disease, the doctor will examine the back especially the lumbosacral region by means of visual inspection, followed by palpitation, and then he will proceed with neurological tests to check the motor reflexes and sensation of the lower extremities
Lab tests
- MRI is the golden standard diagnostic method used to rule out sciatica, because it shows both the soft tissues and bones perfectly and gives a good picture if anything is impinging on nerves or the spinal cord.
- Nerve conduction study to determine the speed of impulses throughout the nerves as a response to a stimulant
- X-rays of the spine and lower back (the lumbosacral region)
- CT scans
2- Treatment and management
How to Relieve Sciatica when Pregnant
Verified by: Dr.Diab (January 7, 2017)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (January 7, 2017). Understanding sciatica. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 3(2). urn:medcoi:article15917.













There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks