Placenta Previa
What is placenta previa and what are the chances of placenta previa?
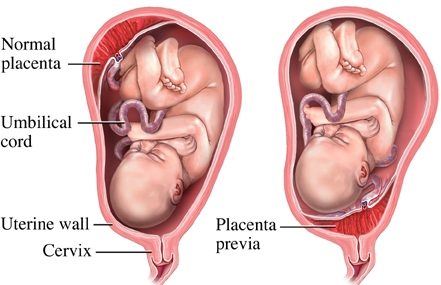
Placenta Previa (предлежание плаценты, انخفاض المشيمة خلال الحمل) is a pathological condition that occurs in approximately 1/200 deliveries in which the placenta is implanted over or near the internal cervical os.
What are the different types of placenta previa?
The three types of placenta previa include:
- Total previa (complete previa) is when the placenta covers the internal cervical os completely.
- Partial previa is when the placenta covers the internal cervical os partially.
- Low-lying placenta or marginal previa is when the placenta encroaches on the internal cervical os.
Placenta previa occurs usually in multiparas, in patients who have had a C-section (cesarean section), or in females with uterine fibroids or other uterine abnormalities that inhibit normal implantation.
Symptoms
What are the symptoms of placenta previa?
Sudden and acute bright red vaginal bleeding during late pregnancy (after the 20th week of pregnancy), it can be total or partial previa, especially in women who have previously had a cesarean section (C-section) or in women with fibroids or other uterine abnormalities that inhibit normal implantation.
Bleeding may range in severity from light to severe
Painless bleeding that can be associated with uterine contractions and abdominal pain
Causes
What are the causes of placenta previa?
Placenta previa is caused by an abnormality in which the lower uterine segment thins as it begins to stretch to accommodate the growing embryo.
Other causes include scarring of the upper lining tissues of the uterus, especially in women who have had multiple dilation and curettage procedures (D&C procedures) or in women with two prior cesarean deliveries. Uterine factors that can predispose to placenta previa can also include any type of surgery involving the uterus
Treatment
- Classical treatment
How to treat placenta previa?
- Bed rest regimen if the bleeding is minor and if delivery term is not close.
- Abstain from sex, as sex during pregnancy will increase the risk of antepartum hemorrhage (APH) and can increase the risk of placental abruption in women with placenta previa. Pregnant women have been advised to abstain during the second and third trimesters to avoid pregnancy complications
- Delivery is indicated if bleeding is moderate or heavy when the fetus reaches his 34week, c-section is the operation standard, but if the head is compressing the placenta or if the woman is having a low lying placenta then vaginal delivery is recommended. In a woman at high risk of emergency transfusion, such as placenta praevia collect blood in advance so that it can be used in case of emergency
Next steps management
How to diagnose placenta previa and when can you be diagnosed with placenta previa?
Most cases of placenta previa are diagnosed during a routine mid-trimester fetal ultrasound examination (the routine 20-week ultrasound scan). Confirmation of the diagnosis may require a combination of abdominal ultrasound and transvaginal ultrasound, which is done by placing a slender, wand-like device inside the vagina.
Ultrasound examination is performed to detect the position of the placenta. The initial ultrasound examination may detect a placenta previa or a low-lying placenta, but in most pregnancies, the condition resolves as the uterus enlarges.
Verified by: Dr.Diab (November 28, 2017)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (November 28, 2017). What is Placenta Previa? Causes Symptoms and Treatment. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 9(2). urn:medcoi:article15547.













There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks