Technical validation of CT Perfusion in stroke management (CTP)
[pro_ad_display_adzone id=”17752″]
Disease and/or Condition: Acute Stroke
Precision, Repeatability and Reproducibility of CT Perfusion
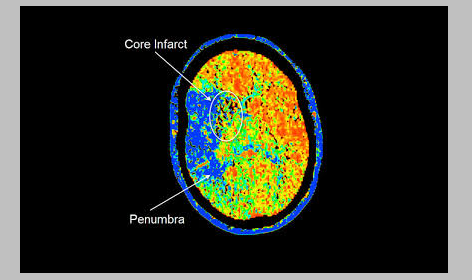
CTP has proven efficacy in evaluating stroke, it is the most relevant diagnostic imaging procedure in terms of accessibility, speed, and ability to explore the ischemic penumbra (identifying the salvageable ischemic penumbra from the unsalvageable core infarct), or the identification of the tissue at risk allowing the expansion of the beneficial therapeutic window beyond the allocated and globally accepted 4.5 hours, thus allowing the selection of individuals who will benefit from therapy from those in whom treatment is less likely to bring the desired results. However, CTP interpretation can be complex.
- CT perfusion initiated following an initial NECT has proven its efficacy and currently is a supported strategy for imaging tissue at risk (infarct core assessment on rCBF map)[2]
Patient Safety and Experience
- Low sensitivity of MTT maps (mean transit time) in predicting an ischemic stroke, which can be detected on DWI sequence
- The relatively low-contrast to noise ratio promotes vulnerability to relics, and decreases sensitivity in general.
Accuracy
- Proven a positive prognosis in stroke patients with favorable penumbral pattern in the therapeutic window outside the accepted beneficial time-limits (outside the initial 4.5 hrs range) regardless of recanalization
- A recent study proved that penumbra volume based on CTP was an authentic and independent predictor of clinical outcome in a three months period along with the status of recanalization. This study also confirmed that the penumbra volume based on CT perfusion could not be precisely evaluated by Nonenhanced Head CT, CT Angiography, or clinical parameters [3].
Availability
- Rapid availability, Relative cost efficacy, and high potentials for quantitative assessment in the field of stroke management if compared to MRI
- CTP is available in most hospitals and healthcare centers with stroke services.
References
- emc.healthyorthodoxmedicine
- W.S. Smith, H. C. Roberts, N. A. Chuang et al., “Safety and feasibility of a CT protocol for acute stroke: combined CT, CT angiography, and CT perfusion imaging in 53 consecutive patients,” American Journal of Neuroradiology, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 688–690, 2003
- G. Zhu, P. Michel, A. Aghaebrahim et al., “Computed tomography workup of patients suspected of acute ischemic stroke: perfusion computed tomography adds value compared with clinical evaluation, noncontrast computed tomography, and computed tomography angiogram in terms of predicting outcome,” Stroke, vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 1049–1055, 2013
Verified by: Dr.Diab (January 18, 2017)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (January 18, 2017). Technical validation of CT Perfusion in stroke management. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 2(2). urn:medcoi:article17248.













There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks