Benign Breast Tumors | Fibroadenomas
Definition
What is a benign breast tumor?
Benign Breast Tumors are very common conditions caused by benign fibrocystic changes in breast tissue (fibrosis and/or cysts), and most women have them, in fact, unlike breast cancers, benign breast tumors are not life threatening. However, some breast lumps are linked with a higher tendency to become cancerous (malignant) later on. Around one third of women between the ages of 35 and 50 experience breast cysts.
Breast cysts or lumps are movable, benign noncancerous growths. A breast lump is a localized swelling, bulge, growth, or bump in the breast that may be felt as a single firm or hard mass in one or both breasts.
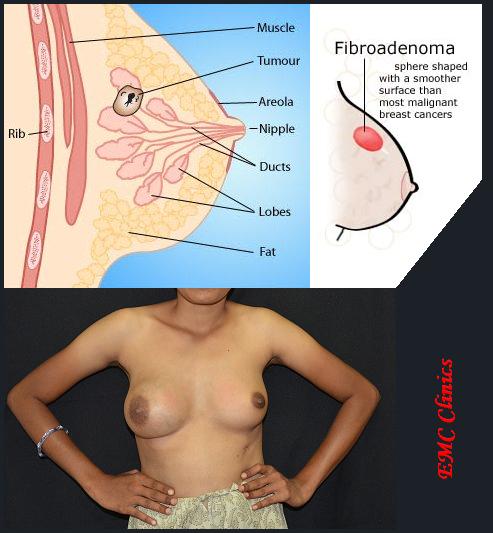
A breast lump is a round firm mass (Fibroadenoma or intraductal papilloma) that moves a little when you press on it and may cause pain when touched (tenderness to touch).
It is very important to identify the signs of breast tumors and to be able to investigate it yourselves without the need of a healthcare professional. Breast lumps are a concern and should be checked because it may be a sign of breast cancer. However, in most cases, lumps found in breast are benign tumors, such as cysts or fibroadenomas.
If you find a lump in your breast during a breast self-exam then it is your first responsibility to visit a doctor, as finding a lump in your breast can be alarming; However, don’t get panicked because in most cases, the lumps found in breast are benign.
In the united states, benign breast lesions account for 80% of 1.6 million breast biopsies performed yearly.[2]
Causes
What can cause a lump in your breast?
There are many possible causes for a breast lump; however, in most cases, breast lumps are caused by infections, breast traumas, noncancerous growths, and cancer. Other potential causes include:
- Medication side effects, adverse effects related to drugs
- Genetic predisposition, a family history of breast cancer in first-degree relatives
- Poor hygiene and wearing dirty clothes, especially dirty bras
- Wearing tight bras
- Sexual abuse or perversion, unhealthy practices or role-playing involving bdsm (bondage and sadomasochism)
- Bigger breast sizes
- Multipara mothers, or breastfeeding two babies at the same time
What are the different types of breast lumps?
Common types of benign breast lumps include cysts (sacs of fluid that build up in your breast tissue), intraductal papillomas and fibroadenomas.
Fibrocystic breast lumps are common in women ages 25 to 50. These benign breast tumors are made up of both glandular tissue and stromal cells (connective tissue cells). Fibroadenomas account for 68% of all breast lumps and about 50% of breast biopsies performed every year.
What does an intraductal papilloma feel like?
Solitary papillomas (solitary intraductal papillomas) are single benign neoplasms or masses that often grow in the milk ducts near the nipple. An intraductal papilloma is a small benign mass near the nipple that may cause clear nipple discharge or bleeding, especially when an intraductal papilloma breaks a duct.
Can intraductal papilloma turn into cancer?
Solitary intraductal papillomas are not associated with a higher risk of breast cancer. However, when an intraductal papilloma contains atypical cells, it may increase the risk of developing breast cancer in the future.
Mammary hamartoma or fibroadenolipoma is a rare slow-growing breast tumor that accounts for approximately 1-4.8% of all breast lumps. It is common in all age groups after puberty.
Symptoms
What are the symptoms of a benign breast tumor?
In most cases, benign breast conditions mimic the symptoms of breast cancer. Common symptoms of benign breast lumps include:
Changes in size or shape of breast, if you notice that the size or shape of your breast has changed. The breasts will often feel tender and/or swollen
Breast changes, if you notice redness, puckering or dimpling in the skin of the breasts or if you find a mass or any change in your breast or underarm area
If you notice a lump in one breast, it is recommended to check your other breast, to compare your breasts and to check if you have uneven breasts
If your breast is getting thicker or having lumps. Thickening of the breast tissue can be due to fibrocystic changes.
Nipple changes, if you notice that your areola (the area surrounding the nipple) or nipple has changed
Lymphadenopathy, especially under the armpit
Tender breast, if you feel pain in your breast
Nipple discharge in one or both nipples.
Diagnosis
How to detect breast lumps?
In most cases, benign breast lumps are accidentally found during breast self-exam or during a breast exam by doctors in medical care. If you find a lump in your breast, it’s best to see your doctor to be sure it’s not breast cancer.

How to diagnose lumps in breast and what tests are done to diagnose a breast lump?
Depending upon your age and symptoms your doctor may suggest different kinds of tests. Tests and procedures used to diagnose breast lumps include:
A Mammogram is an x-ray imaging test used to diagnose breast lumps in which low-energy X-rays are used to examine the breast and to look for breast lumps.
An Ultrasound is a medical test used to diagnose breast lumps in which sound waves are used to examine the inside structure of your breasts and to look for breast tumors.
Core needle biopsy or fine needle aspiration is a diagnostic procedure in which a small amount of the breast tumor (aspirate) is taken with a fine needle (a thin 23-25 gauge). After an FNA biopsy, the cells aspirated from the lesion(s) will be examined under a microscope.
Treatment of Benign Breast Tumor
How to treat benign breast lumps?
Breast lumps (lipomas, hyperplasias and fibroadenomas) usually don’t require treatment unless they are producing symptoms. In most cases, breast lumps (masses and/or cysts) resolve or shrink spontaneously.
Breast cysts may persist and remain stable for many years; however, a fine needle aspiration (FNA) can be used to aspirate a cyst and to remove it completely, especially if the cyst is large and tender. Moreover, a fine needle aspiration biopsy is done to help determine the nature of the lesion and to plan treatment if necessary (diagnosis of breast tumor).
Benign breast tumors can grow to be large in size, in this case, treatments are directed at eliminating and removing these large breast tumors (large lipomas, hyperplasias or fibroadenomas) because otherwise they will grow bigger.
After removing these lumps, all the tissue biospecimens are then sent to the laboratory or pathology lab as soon as possible after collection for further laboratory investigation and to aid diagnosis. Also, if lumps are phyllodes then it is advised to remove the tumor(s) by tumorectomy (surgical removal of a tumor), as phyllodes may grow quite quickly and quite large.
Before initiating treatment (breast lump removal), patients undergo routine checks to make sure that they have no current infections or abscesses. If infection is present, patients should receive empirical oral or parenteral antimicrobial treatment.
If an abscess is present, abscess (Incision and Drainage) should be done to drain out the pus.
Your treatment depends on the type of tumor you have, and on how severe your symptoms are.
Prevention
How to prevent malignant breast lumps?
Up till now, there isn’t any evidence that certain lifestyle changes, such as maintaining good personal hygiene habits and eating a healthy, balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables and foods high in fiber can reduce the risk of benign breast tumor. However, four in ten cancers can be prevented, largely through lifestyle changes, so it is a good idea to maintain a healthy lifestyle, as simple lifestyle changes can make a big difference. It is recommended to reduce alcohol consumption, to quit smoking and to reduce intake of processed meat, salt, and salt-preserved foods because these changes can reduce the risk of cancer.
For women, moderate drinking is defined as no more than seven drinks per week.
References
Verified by: Dr.Diab (November 18, 2017)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (November 18, 2017). Benign Breast Tumors Causes Symptoms and Treatment. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 28(2). urn:medcoi:article1142.











There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks