Dyspareunia Causes Symptoms and Treatment
What is dyspareunia caused by?
Dyspareunia (Painful coitus, pain during completed or attempted vaginal penetration) is a gynecological disorder caused by psychological, pathological, physiological or traumatic factors, it is characterized by introital pain occurring before, during, or after intercourse
Symptoms
What are the symptoms of dyspareunia?
Common symptoms of dyspareunia include:
- Pain during, before or after intercourse, pain may last hours after intercourse
- Pain with every penetration
- Pain while putting in a tampon
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Vaginal discomfort
- Deep pain during thrusting
- Emotional liability
- Bad mood
- Bad appetite
- Headache
Causes
What is the cause of dyspareunia?
Dyspareunia is mainly caused by chronic inflammation or infections, such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), sexually transmitted infections (STIs), vaginal yeast infections, or vulvar vestibulitis syndrome (vestibulodynia or vestibular adenitis, VVS), an inflammation around the vaginal opening that is characterized by severe pain during attempted vaginal entry. Less commonly, dyspareunia may be caused by physiological factors, such as traumas, or erosions and by functional factors, such as decreased moistening and lubrication of the vagina due to decreased estrogen levels
What are the major causes of dyspareunia?
Below is a list of the major causes
Traumatic causes
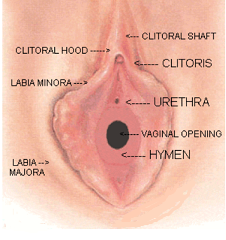
- Hymenal tears
- Laceration of the fourchette
- Bruising of the urethral meatus
- Painful superficial ulcerations following an injury
- Forceful pressure against a sensitive urethra during coitus
Physiological causes
- Inadequate lubrication, usually secondary to improper or insufficient foreplay
- Improper intromission
- Allergic reactions to the contents of condoms, contraceptive foams and jellies
- Irritation due to the use of improperly fitted or inadequately lubricated condoms
Pathological causes
- Introital lesions due to underlying inflammatory conditions, such as vestibulitis
- Infections, such as bartholin abscesses and cysts
- Inflammation of labia apocrine sweat glands
- Dermatologic disorders, such as lichen sclerosis
Anatomical causes
- Abnormalities of the female genital tract, such as a rigid hymen or congenital septum
Psychological causes
- Vaginismus
Treatment
How to treat dyspareunia?
- History checkup and examination of both partners
- Sexual activity case study, frank explanation of the sexual intercourse and the sexual organs
- Guidance for the couple on how to have sex properly
- An anesthetic ointment, such as 1% lidocaine or 1% dibucaine can be used to alleviate postcoital pain
- The patient must refrain from sex, especially if an injury is confirmed
- Vaginal perineal skin care, cleaning and caring for your perineum, the region of the body between the anus and the vulva
- Antihistamines, such as fexofenadine (Allegra), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), certirizine (Zyrtec), loratadine (Claritin), loratadine ODT (Alavert, Tavist ND), can be used to relieve the itching
- Over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal creams and ointments, such as clotrimazole, miconazole nitrate, butenafine hydrochloride, tolnaftate, and terbinafine hydrochloride, are often prescribed for vaginal irritations and swelling
- Over-the-counter pain medicine, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), acetaminophen (Tylenol), or naproxen (Aleve), are often prescribed to relieve pain. Common Adult Dose: 500mg of acetaminophen orally every 4-6 hrs
- Oral estrogen replacement therapy is a first line option to alleviate vulvovaginal symptoms if dyspareunia persists after treatment and if there are no contraindications to HRT treatment
Next steps management
How to diagnose dyspareunia?
- Clinical interview
- Gynecological examination
- Ultrasound of the abdomen/pelvis to evaluate the uterus, cervix, ovaries, fallopian tubes and bladder
- A hormone panel test, to test estrogen, progesterone, FSH and LH levels
References
Verified by: Dr.Diab (December 18, 2017)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (December 18, 2017). What is Dyspareunia? Causes Symptoms and Treatment. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 5(2). urn:medcoi:article15741.













There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks