Ectopic Pregnancy
Definition
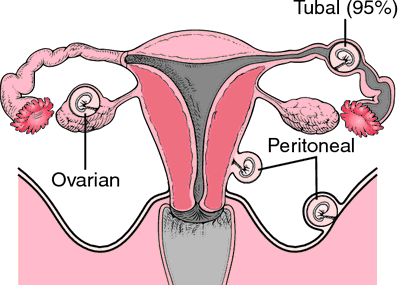
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy (внематочная беременность, الحمل خارج الرحم) is an abnormal pregnancy in which implantation occurs outside the uterine cavity in the uterine tube (fallopian tube), ovary, cervix, abdominal or pelvic cavity.
Symptoms
What are the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy?
Early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy usually occur six to eight weeks after a missed period. Common symptoms of an extopic pregnancy include:
- Acute pelvic pain and abdominal cramps
- Adnexal mass
- Irregular menses after a three weeks late menstruation
- Nausea and vomiting
- Lower abdominal pain on one side of your body
- Rectalgia or rectal pain
- Dizziness or weakness
How does an ectopic pregnancy feel like?
Symptoms and signs of an ectopic pregnancy may mimic the early signs of a normal period, an ectopic pregnancy may feel like you’re having a miscarriage, with abdominal cramping and slight vaginal bleeding. In most cases, however, women with ectopic pregnancy usually experience the same symptoms as in a normal pregnancy, such as a late or missed period, or sore breasts, etc.
About 10% of women with ectopic pregnancy are asymptomatic
How long can you go with an ectopic pregnancy?
In most cases, the embryonic mass (ectopic growth) usually ruptures after about 6 to 16 weeks. When an ectopic pregnancy ruptures, it may lead to severe life threatening conditions, such as severe internal bleeding, a leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide.
What is the first sign of a miscarriage?
Early signs of miscarriage include vaginal bleeding with lower abdominal pain and pelvic cramps. In most cases, you may have pelvic cramps with a persistent, dull ache in your lower back.
Causes
What are the causes of an ectopic pregnancy?
In most cases, an ectopic pregnancy is believed to be caused by one or more of the following:
- Pelvic adhesions remain a common cause of infertility in females. In most cases, adhesions are caused by chronic inflammation or irritation of the pelvic tissues from a common disease, such as endometriosis
- STI following a surgical procedure
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or tubal infection from a sexually transmitted disease, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea
- Hormonal imbalance
- Endometriosis can lead to fallopian tube blockage due to the formation of scar tissue or adhesions
- Problems with the tube walls. In norm, the tube walls tighten and carry the fertilized egg into the uterus
- Genetic defects
Treatment
Classical treatment
What are the treatment options for ectopic pregnancies and how to treat an ectopic pregnancy?
Expectant management and monitoring by a doctor for two weeks, the clinical manifestations of ectopic pregnancy, such as pain or bleeding should resolve within 2 weeks. However, if you haven’t had any bleeding or pain within 7-14 days, or if the clinical signs of ectopic pregnancy get worse after 7-10 days, this could mean that the abortion hasn’t begun or hasn’t completely finished.
Laparoscopic surgical removal of an ectopic growth or the fallopian tube section is performed after confirming a diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. Alternatively, a tubal pregnancy can be removed from a fallopian tube by using laparoendoscopic single site surgery (LESS) or laparoscopic salpingectomy.
Low-dose chemotherapy with methotrexate is also used in the treatment of ectopic pregnancies. Patients with a diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy are given methotrexate 50mg/m2 IM single dose followed by 800 mcg misoprostol vaginally. Treatment of ectopic pregnancy with methotrexate (MTX) is recommended if the mass has not ruptured or if the mass is less than 3.5 cm in diameter and if fetal heart rate is absent on ultrasound. Misoprostol should be given 5-6 days after initiation of treatment with methotrexate.
Monitoring Beta HCG levels (serum beta-human chorionic gonadotropin levels) and routine abdominal ultrasound are routine first-line therapeutic measures for sonographically confirmed ectopic pregnancies.
- Alternative treatment
Next steps management
How early can an ectopic pregnancy be diagnosed?
A normal pregnancy is visible 6 weeks after the last menstrual period (LMP). However, an ectopic pregnancy is suggested if there are no signs of a fetus in the uterus as expected. In most ectopic pregnancies, hCG levels are either elevated or rising.
How do you know you have an ectopic pregnancy and how is an ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
To confirm a diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy, your doctor will likely perform the following tests:
History and physical examination. A complete physical examination includes careful inspection of the patient, palpation, percussion, and auscultation to unveil the data necessary for patient diagnosis and management.
A pelvic exam to evaluate the size of the uterus and to determine if there is any tenderness or growths while you palpate the abdomen
Diagnostic tests to confirm the situation:
What is the hCG quantitative blood test?
The hCG quantitative blood test is a blood test that measures the level of hCG hormone present in a sample of your blood. The human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone produced during pregnancy. This test should be repeated two days later.
Imaging studies, such as a pelvic ultrasound, a transvaginal ultrasound is gold standard procedure used to show where a pregnancy is located.
Verified by: Dr.Diab (November 20, 2017)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (November 20, 2017). What is an Ectopic Pregnancy? Causes Symptoms and Treatment. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 7(2). urn:medcoi:article15577.













There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks