Endometrial Cancer (Adenomatosis)
Definition
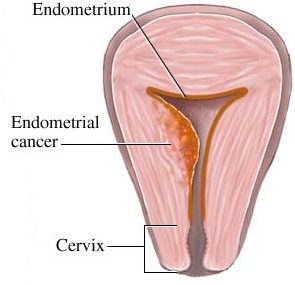
Endometrial cancer (рак эндометрия, рак тела матки, سرطان بطانة الرحم) is one of the most common gynecologic malignancies in the USA that mainly affects postmenopausal women, with incidence peaking between ages 50 and 55. It is considered the fourth most common malignancy affecting females after breast, colorectal and lung cancers.
About 25% of cases of endometrial carcinoma occur in women under 40 years of age (before the menopause)
Only 5% of the newly diagnosed cases occur among women younger than 40 years old. About 40,000 new cases of endometrial cancer are diagnosed yearly since 2000.
What is the survival rate of endometrial cancer?
The 5-year survival rate for women with endometrial cancer is 84% for white women and 62% for black women because black women are less likely to be diagnosed at an early stage
Symptoms
What are the warning signs of endometrial cancer?
Most women with endometrial cancer are asymptomatic, however, in some women, symptoms may include:
- Postmenopausal heavy bleeding with or without abdominal pain, this symptom is present in 90% of women with endometrial carcinoma
- Postcoital spotting (bleeding after sex) and unusual vaginal discharge, which may be blood-tinged or watery
- Nonmenstrual bleeding and intermenstrual bleeding (IMB), especially in women under 40 years of age
- Menorrhagia or abnormally heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Depression
- Bad appetite
- Symptoms and signs of anemia, symptoms and signs of anemia caused by endometrial cancer could include: easy fatigue, unusually rapid heart beat, dyspnea, dizziness, pale skin, insomnia, lightheadedness, headache and leg cramps. Anemia may occur as a direct result of the cancer
- Pelvic pain, or feeling a mass
- Unexplained weight loss
Causes
What are the causes of endometrial cancer?
Underlying uterine abnormalities are believed to play an important role in the evolution of endometrial cancer, such as chronic endometritis and endometrial hyperplasia, a chronic disorder that develops in females with chronic hyperestrogenism and in women with low progesterone levels (hypoprogesteronism), a situation common in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (pcos), neuroendocrine syndrome, hormone dependent ovarian tumors and in women who do not ovulate (anovulation).
Treatment
How to treat endometrial cancer?
- Classical treatment
- Radiotherapy to kill cancer cells
- Hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo oophorectomy
- Surgery to remove lymph nodes (Lymphadenectomy)
- Hormone therapy, Progestin hormone therapy to suppress tumor growth. Norkolut( norethisterone) is prescribed in a dose of 5- 10 mg (1-2 tablets) per day, from 5th day to 25th day of the menstrual cycle
- Chemotherapy (chemo) is used to kill cancer cells and stop tumors from growing, it may be used for many types of metastatic cancer
- Surgical exploration treatment whenever indicated
Next steps management
How to diagnose endometrial cancer?
- Routine pelvic exam during which the physician evaluates the size and position of the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. Routine pelvic exams can improve the chance of early detection in asymptomatic average risk women
- Pelvic ultrasound is often one of the first imaging tests used to evaluate the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes in women with a possible uterine problem. TVUS images can be used to detect a uterine mass, or to see if the endometrium is thicker than usual, which can be a sign of endometrial cancer
- Hysteroscopy and separate diagnostic curettage
- Blood testing for cancer markers, such as the CA-125 blood test. CA 125 is a tumor marker that may be found in the blood in some cases of uterine cancer
- Looking for extrauterine metastases by biopsy or excision. These include lymph node metastasis, intraperitoneal spread, and adnexal metastasis
- Peritoneal Fluid Analysis, sampling of peritoneal fluid (through an abdominal incision) for cytological evaluation, sampling of the pelvic and paraaortic lymph nodes. All patients with a suspicious lymph node should be referred to a doctor, removal of suspicious lymph nodes can reduce the risk of development into a malignancy
- A pap test (a pap smear) may show signs of an abnormal endometrium; however, these tests are not used to screen for endometrial cancer
If endometrial cancer is confirmed after examining uterine tissue samples (biopsy) or if cervical involvement suspected, a radical hysterectomy with pelvic and paraaortic lymph node dissection should be performed
References
Verified by: Dr.Diab (December 19, 2017)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (December 19, 2017). Endometrial Cancer Causes Symptoms and Treatment. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 4(2). urn:medcoi:article15568.













There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks