Human papillomavirus infection “HPV vaginal infection” Definition, Symptoms and Treatment
Definition
What is papillomavirus infection?
Human Papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is a common highly contagious viral infection affecting the humans, it is characterized by lesions appearing on the mucous walls of the oral, anal, and genital cavities; Moreover, many strains of the virus are believed to cause typical warts on the fingers and feet.[2]
HPV vaginal infection is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases that affect both girls and women evenly.
Description
What is the cause of hpv infection?
More than 60 subtypes of HPV virus have already been recognized, some of these subtypes are associated with cancer and precancerous conditions. The herpes virus that can be sexually transmitted, is frequently present in patients suffering of cervical cancer.
HPV infection is spread through sexual contact (vaginal, anal, and oral ) with someone who has an HPV infection.
Facts
How does infection with human papillomavirus virus increase the risk of cervical cancer?
About one-third of the HPV viruses can be transmitted by sexual contact.
Rarely HPV causes clogged pores and HPV skin warts. Several types of HPV (HPV – types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, and 39) may lead to HPV vaginal warts, the most recognizable symptom of HPV infection. Superinfection of several HPV subtypes is common within the genital warts.

Other subtypes of HPV are highly associated with the development of cervical cancer, and are believed to play an enormous role in the development of several genital disorders as well. HPV was found in 99.7% of cervical squamous cell cancer cases.[1]
Lab tests are used to rule out malignancy in HPV warts, especially in patients diagnosed with HPV infection.
Despite the powerful links between HPV infection and cervical malignancy, most HPV infections resolve spontaneously and do not cause intensifying lesions. Although HPV contamination is common, cancer eventually evolves in a little percentage of patients only. Other cancerogenic factors that coincide with HPV infection include:
- Cigarette smoking
- Extensive utilization of oral contraceptives (chronic usage of contraceptives for more than 4 years increases the risk to develop cervical cancer)
- Sex in young age
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Being infected with another STD
Symptoms
What are the symptoms of hpv infection?
Such as many other STDs, HPV genital warts triggered by HPV antigen do not cause symptoms in most cases. One local observational research was held on a group of females with Positive HPV Test Results, the research group included 43 sexually active females (8 Ethiopian, 7 kenyan, 17 syrian, 4 srilankan, 7 Bangladeshi, prostitutes) aged between 18-40, results obtained following a period of three months of visual monitoring showed that about half of women presenting with HPV genital lesions had no visible signs nor symptoms. Results documented by EMC.[3]
In many cases, nevertheless, small, circular and rigid spots, that are easily visible to the eye, develop within three to nine weeks after sexual contact.

In women, HPV lesions can be seen on the labia majora, labia minora (external lips of the vagina), as well as in the internal vaginal tunnel, infection can spread throughout the uterus, or it can concentrate just around the anus (Perianal HPV infection). Anogenital HPV infections might be itchy.[4][3]

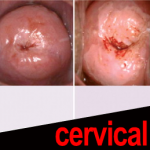
Women additionally develop cervical warts, that are flat lesions invisible in their early stages. HPV cervical warts are the main cause of irregular Pap smear tests.
HPV warts on the skin (face, fingers, hip, legs and feet) may be itchy or slightly tender “painful to touch”; However, these warts are usually asymptomatic.

What does HPV on a man look like?
In men, genital warts can form on or around the penis, warts usually appear as a group of bumps on or around the penis or the anus; However, men can also have a single small bump that may appear on or around the penis or on the anus. Genital warts can range in size from small pinhead warts to large flat ones. In most cases, a genital wart is a raised skin lesion that can look like the top of a cauliflower.
Diagnosis
How to diagnose hpv infection?
If you suspect having HPV vaginal warts, get in touch with your physician so that to evaluate the lesion(s), and to rule out other causes of similar symptoms before initiating a proper treatment.
How to test for hpv infection?
HPV Genital warts are often diagnosed by immediate visual examination. However, a pelvic examination is necessary for the diagnosis of cervical infections, a Pap smear is the gold standard test of choice used for the diagnosis of HPV infection. HPV skin warts and clogged pores (face, hand, legs, and feet) are diagnosed clinically.
Treatment
How to treat hpv infection?
How to treat hpv skin warts?
Typical HPV skin warts and clogged pores (pimples) can be treated by means of freezing cryosurgery, or by the application of salicylic acid products (Occlusal, Viranol). Recurrences are common and laser treatment might be effective in severe conditions.[10][11]
Genital warts frequently result from clusters and may accumulate into larger parts of the vaginal tissue. These conditions often reappear right after therapy. Depending on factors for example their size and area, vaginal warts are handled in a number of ways:
A physician may suggest a treatment along with a chemical, for an example applications of 20% podophyllin solution, which is applied to the impacted region and washed away after several hours. Podophyllin should not be used during pregnancy because it is absorbed through the skin pores, which may cause birth abnormalities.[8][9]
Small warts can be removed by freezing (with liquid nitrogen) or burning (electrodesiccation). Imiquimod, a five percent lotion, which acts an interferon inducer, offers moderate activity in cleaning external HPV genital warts.[7]
Surgical treatment is occasionally required to eliminate large resistant warts, which have not responded to therapy. Worldwide many Doctors use laser beam surgery to get rid of HPV genital warts.
Cervical contamination and cellular changes mandate the use of colposcopy, a painless evaluation technique during which a lighted magnifier device is used to explore the female reproductive system.
In some instances, it is necessary to do a biopsy of the cervical tissue. This requires taking a small sample of cervical tissue for microscopic evaluation, and based on the nature of the cervical lesion, cauterization, freezing (cryosurgery), laser, or even surgery might be necessary.
Precautions
How to prevent hpv infection?
HPV testing, which is used to look for the presence of high risk HPV types in cervical cells is mandated for all young girls, and sexually active women.for a healthy life free of Human papillomavirus infection.[5][6]
References
Verified by: Dr.Diab (September 16, 2018)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (September 16, 2018). Human Papillomavirus Infection Definition, Symptoms and Treatment. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 16(2). urn:medcoi:article1108.











One comment
Or use one of these social networks