Postmortem Changes and Stages of Decomposition
What happens to our bodies when we die?
Clinical death occurs when vital body organs fail to function properly, so our body starts deteriorating as soon as our brain stops functioning and when our heart stops beating; however, biodegradation occurs at different rates depending on the circumstances surrounding death (tragic death, homicide, suicide, terminal illness, etc.), the environmental conditions at the time of the accident (weather, car and road conditions, cellular health and body condition, etc.) and the environmental conditions surrounding the corpse (weather conditions such as moisture or dryness, burial conditions, materials surrounding the corpse, embalming, the nature of the soil, type of coffin wood, etc.).
Postmortem changes timeline
Primary relaxation or flaccidity occurs within minutes after death and it lasts for one to two hours.
1- Pallor mortis is the first stage of death that occurs in people with light skin, it is characterized by paleness that occurs immediately after death.

2- Algor mortis (or the death chill) generally sets in around two hours after death. The body temperature drops about 0.83 degrees Celsius (1.5 degrees Fahrenheit) per hour until it cools to the surrounding temperature.
How long does it take for a dead body to get cold?
After death, the temperature of the body remains raised for about two hours (postmorten caloricity).
Algor mortis (or the death chill) is the second stage of death, it generally sets in around two hours after death as the heart stops beating, and the body temperature drops about 1.5 degrees Fahrenheit (0.83 degrees Celsius) per hour until it reaches room temperature.
Factors affecting the rate of cooling
- The body type of the dead person, whether obese, slim, or muscular.
- The difference in temperature between the corpse and the medium.
- The environment surrounding the corpse.
- Covering on or around the corpse.
3- Rigor mortis (postpartum body stiffness) generally sets in about three to four hours after death, peaks at 12 hours, and dissipates after 48 hours due to decomposition. High body temperature may cause rigor mortis to develop more rapidly.

What is rigor mortis caused by and how long does it last?
Oyxygen plays a vital role in the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) that provides energy for sliding the actin and myosin filaments of striated muscle over each (the sliding filament model) by hydrolysing ATP into ADP+Pi, which enables the Myosin to pull the Actin filaments inwards and so shortening the muscle (muscle contraction); however, after death, your body’s supply of oxygen will be depleted and the body enters rigor mortis because the ATP concentration diminishes. ATP is required to cause separation of the actin-myosin cross-bridges during relaxation of muscle.
Rigor mortis is the third stage of death, in which a dead body becomes stiff and hard to move, it occurs due to chemical changes in the muscles postmortem. Rigor mortis generally sets in about three to four hours after death, peaks at 12 hours, and dissipates after 48 hours, in most cases, it lasts for up to eighteen hours.
What are the different stages of rigor mortis?
According to the Medicolegal Death Investigators Training Manual, there are six stages of rigor mortis in humans.
4- Livor mortis or hypostasis is the fourth stage of death, it occurs within minutes to hours after death due to blood settling in different parts of the body. Some bodies show Tardieu spots (dark purple spots) in dependent areas, due to ruptured capillaries. However, in most cases, the skin gets purple and waxy 20 to 30 minutes after death.

What Color do you turn when you die?
Within minutes to hours after death, and the overall color of the body changes, the skin gets purple and waxy in about 30 minutes after death.

Pale skin in areas exposed to pressure, as mechanical compression prevents blood flow in the blood vessels. These areas will not show lividity.

Postmortem discoloration of the skin, lips, fingernails, and toenails occurs within minutes to hours after death due to livor mortis or hypostasis. The lips, fingernails, and toenails fade to a pale color or turn white as the blood leaves and the flow of blood around your body ceases.
Postmortem discoloration of the hands and feet, the hands and feet turn blue. Moreover, bluish-purple and purplish-red discoloration (postmortem hypostasis) appears on dependent body parts, it is caused by pooling of blood in the vessels under the influence of gravity.
Postmortem lividity (postmortem staining or hypostasis) occurs within minutes after death during which blood pools at the lowest parts of the body leaving a dark purple stain, lividity is fixed in around six hours after death as blood vessels begin to break down within the body. However, it can be altered by moving the body in the first 6 hours after death.

Postmortem lividity (hypostasis) is the pooling of blood under the influence of gravity during which blood pools at the lowest parts of the body leaving a dark purple or black stain (postmortem staining), lividity can be altered by moving the body in the first 6 hours after death, however, after this period lividity is fixed as blood vessels begin to break down within the body.

5- Putrefaction or decomposition is the fifth and final stage following death, this process involves the decomposition of organic matter and soft tissues (proteins, carbohydrates, and fats) by the action of bacterial enzymes (enzymes produced by anaerobic bacteria such as clostridium perfringens or cl welchii, and enzymes derived from fungi such as aspergillus, or penicillium, etc.), which causes the deterioration of the tissues and organs and the breakdown of the cohesiveness between tissues due to the release of gases that infiltrate the body’s tissues. In advanced putrefaction, the liquefaction of most organs because the texture of an organ can be completely dissolved.

Microorganisms enter body shortly after death because the immune cells are absent and spread through the blood vessels using the carbohydrates and proteins as culture media.

How long does it take for putrefaction to occur?
Black putrefaction occurs in the early postmortem interval (days 10-20), which is when parts of the body undergo a black discoloration, and in this period noxious odors are released because the decaying body releases chemicals like putrescine and cadaverine.

By the second week after death (2 weeks postmortem), the abdomen gets distended or bloated to its maximum stretching capacity, as internal gas builds up in the abdominal cavity and pressure nears maximum capacity.

By the third week after death (3 weeks postmortem), in this period, tissues get softened, and pressure keeps building up in the abdominal cavity, and in the end the cavities and organs eventually burst.

What is the process of decomposition?
Decomposition is the natural process of dead animal, in which, organic matter is broken down into a less complicated chemical structure by oxidation, rotting, or putrefaction, which is usually carried out by invertebrates, fungi and bacteria (anaerobic or aerobic bacteria).

What are the stages of decomposition?
Stages of decomposition of human body
Several stages describe the process of decomposition in the humans and vertebrate animals. The stages of decomposition occur simultaneously with autolysis and putrefaction.
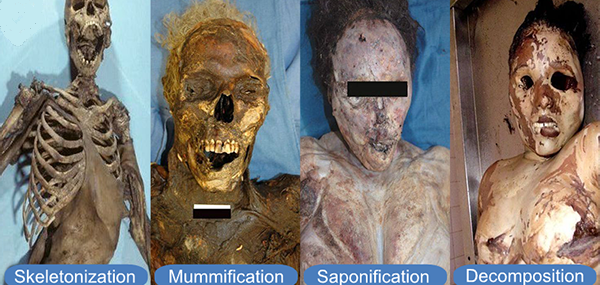
The five stages of human decomposition include: Initial decay, bloat, active decay, advanced decay, and skeletonization or mummification.
1- Initial decay and Autolysis: cells self digest (autolysis) and bacteria proliferate, the destruction of cells by intracellular enzymes released by lysosomes.
2- Bloat and Marbling: gases accumulate due to bacterial activity after which sulfur atoms alter color of blood and skin. Marbling occurs due to breakdown of blood hemoglobin within the blood vessels and capillaries.

Putrefaction or breakdown of tissue due to bacteria, it is characterized by greenish-black discoloration and swelling of the face and neck and by green discoloration of the lower abdomen due to overgrowth of bacteria.

3- Purge and Active Decay: skin ruptures and hair comes out from the scalp, fluid and gas leak out of the body.

Bacterial activity leads to increased gas production that causes diffuse swelling of the body, and the abdomen gets distended or bloated.

The early bloating stage is accompanied by extrusion of reddish-brown purge fluid from the nose and mouth, which is then followed by skin slippage and blistering, and hair slippage from the scalp. Marbling occurs due to breakdown of blood hemoglobin in blood vessels, and in the end of this stage the brain gets partially liquefied.


4- Advanced decay: body shrinks and maggots finish eating, under strong conditions bacteria and insects cannot survive, and instead of continuing to decompose the body they will mummify and the dead body eventually dries up; however, in humid conditions the bacteria and insects continue to feed on the body and they’ll eventually eat it down to a skeleton. Skeletonization usually takes several weeks.

Decomposition (biodegradation) and decay differ a lot from one body to another depending on the conditions surrounding the body, saying so a flock of bacteria and insects will swarm a body immediately if left uncaged, and they can eat much of the flesh within few hours and they may even fray the bones while ripping at it voraciously, finally the body looks like a skeleton with frayed bones partially covered with thick leather or clothing that are left out to decompose in a period of 6-12 months.

Dead tissue decompose more rapidly in hot environments and slowly in cold environments.

What is adipocere formation?
Adipocere (Saponification) is the transformation of body fat such as olein into oleic, palmitic, hydroxystearic, and stearic acids that inhibit putrefactive bacteria, it forms in any site where fatty tissue is present.
Saponification is due to the gradual hydrolysis and hydrogenation of preexisting fats. The process starts under the influence of intrinsic lipases, and is continued by the bacterial hydrolysis of fat tissue.
How is Adipocere formed?
Adipocere is formed by the bacterial hydrolysis of fat tissue in anaerobic environments, which is carried out by anaerobic bacteria of the clostridia group, mainly C. perfringens bacteria, as the bacteria produce lecithinase, which, in turn, facilitates hydrolysis. Acids inhibit putrefactive bacteria, and putrefaction is replaced by the formation of adipocere, which is a permanent firm cast of fatty tissues.

In what conditions does adipocere develop?
Adipocere is either grayish white or yellowish-white in color, it occurs in bodies immersed in water or in damp, warm environment.
Examples of common areas include: The face, breasts, abdomen and buttocks. However, the chest wall, limbs, or other parts of the body may also be affected, and in rare occasions the entire body is converted into adipocere.
How long does adipocere take to develop?
Time Required for Adipocere Formation:
Adipocere is postponed by cold and accelerated by heat; however, it usually occurs in humid or wet environments, the shortest time for its formation is about three weeks in hot dry summer (in temperate countries). Stiffening and swelling of the fat occurs over a period of months. In adipocere, the percentage of fatty acids in total body fat (human depot fat) rise to 20% within a month and over 70% in 90 days.

How long does it take for a body to become mummified under normal circumstances?
Mummification is a process that occurs in extremely dry environments, in which the skin of a corpse turns yellowish-brown or black, and becomes dry and leathery.
An exposed human body in optimum conditions (flies, maggots, ants, dogs, rats, jackals, weather conditions, etc.) can be reduced to bone in 9-10 days, However, extreme circumstances may prevent or delay decay, rapid drying (mummification) of an exposed human body in a hot climate is common, as the weather can become unsuitable for bacterial action.

How long does your brain stay alive after you die?
After death, the heart stops beating, and neurons or brain cells begin to die in about three to four minutes after death. Moreover, brain cells will cease functioning, and brain cell death occurs in about 10 minutes after death and without special treatment postresuscitation, full recovery of the brain to regain lost function after more than three minutes of clinical death at normal body temperature is extremely rare. However, this does not mean that no recovery can occur.
Skin, Bone, and tendon can survive as long as 8 to 12 hours.
How long does it take for the body to decompose?
In most cases, decay starts and finishes within a couple of years; however, full decomposition can take a lot longer depending upon environmental conditions.
Decomposition above ground is four times as fast as underground. Corpses are preserved longer when buried deeper, as long as the ground isn’t waterlogged because decomposition above the ground is twice as fast as when the body is under water.
Decomposition is generally slower in a casket (or coffin), and the body may remain recognizable for up to six months. Corpses that are buried deep can hold traces of the tissues on them, such as tendons and ligaments for about 50 years, as they are more resistant to decomposition, while the internal organs decompose. 3-5 days after death. But within a year all that is usually left is the bones and teeth, with traces of the tissues on them, it takes 40 to 50 years for the bones to become brittle and dry in a coffin. In soil, bones may last for years, while acid peaty soil gradually dissolves the bones.
How long does it take for a body to decompose in a coffin and How long does it take for a body to be a skeleton?
When buried 1,8 meters (6ft) down, in ordinary soil, without a coffin, an unembalmed adult body normally takes 8 – 12 years to decompose to a skeleton. However, if placed in a coffin, the corpse can take 30-50 years to decompose to bones, depending on type of wood used. For example, a solid wood coffin will slow down the decomposition process of human body after burial.
How long does it take for an unburied body to decompose?
Maggots can eat up to 60 percent of a human body within a week, especially if the access of fresh air to the dead body is not cut off. [2]. However, The rate of decay is also affected by the environment in which a dead body is placed. For example, an unburied body on land decomposes twice as fast than if immersed in water.
How long does it take a body to decompose in the water and do bodies decompose faster in water?
If all environmental factors are equal, a body immersed in water decomposes four times faster than if buried in earth; however, a body immersed in cold water under the temperature of 7°C remains almost completely intact after several weeks, and as a recognizable skeleton after five years, as cold water under the temperature of 7°C encourages the formation of adipocere, which is a soapy waxy substance formed by the decomposition of fat in dead bodies subjected to moisture, which, in turn, partially protects the body against decomposition.
How long does it take for human flesh to decompose?
The duration it takes for a dead body to decompose depends on several factors, such as access of fresh air to the dead body, the depth at which the body is buried, humidity, maggots and flies, water, coffin wood material, whether the body is placed in a casket or coffin, etc. any of which may affect the duration it takes to break the body down to ashes. If a dead body is buried around 6 feet deep underground in a coffin, for example, the tissue of the body could even take 50 years to disappear.
Do bones decay over time?
In warm, moist environments, fungi and bacteria will attack the matrix proteins of bone (collagen) and the skeleton will disintegrate over the course of a few years. However, bone also contains bone minerals such as calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate that decompose fastest in well aerated, acidic peaty soils, as they react readily with nitric acid. Calcium phosphate isn’t attacked by microorganisms.
What is the definition of decomposition in biology?
Decaying or decomposition is a term used in biology to describe the breaking down of a material into a less complicated chemical structure by rot, oxidation, rotting, or putrefaction, which is usually caused by fungal or bacterial action.
Why do you poop when you die?
After death, primary relaxation or flaccidity occurs and it lasts for one to two hours. During this stage, all the muscles of the body begin to relax and body flattens over the surface on which it rests; however, muscular response to electrical or mechanical stimuli persists. Once the muscles that constrict your bowels or bladder relax, your body gets rid of waste matter and products it’s been carrying around in three ways: by vomiting, urine leaking, or stool leaking.
Can you ejaculate when you are dead?
During primary flaccidity the muscles that constrict your bowels or bladder relax and passive seeping or leakage of seminal fluid from the prostate gland occurs and your penis will look like it’s ejaculated, and for this reason, we usually find discharge near the penis on a corpse.
When a person is dying can they hear you, and how long does hearing last after death?
Hearing is usually the last sense to go in the dying process, and so it is recommended to talk as if they can hear you, even if they appear to be unconscious. Hearing can last few minutes after death, as brain activity can continue for 10 minutes postmortem.
How do bacteria decompose organic matter?
Decomposition is a complex process caused by fungal or bacterial action, in which organic matter is broken down into carbon dioxide and the mineral forms of nutrients like nitrogen. Microorganisms such as fungi, anaerobic or aerobic bacteria, and protoctists feed on organic material. Saprotrophic nutrition plays an enormous role in in the breakdown of dead animal matter.
Saprotrophic nutrition, is a process of extracellular digestion, in which, chemoautotrophs (a bacterium or a protozoan) obtain energy through chemosynthesis. It is involved in the processing of dead or decayed organic matter.
Postmortem Changes in human body
References
Verified by: Dr.Diab (June 25, 2018)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (June 25, 2018). Postmortem Changes Overview Definitions Scene Findings. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 40(2). urn:medcoi:article18672.











2 comments
Or use one of these social networks