Spermatorrhoea Causes Symptoms and Treatment
What is Spermatorrhoea?
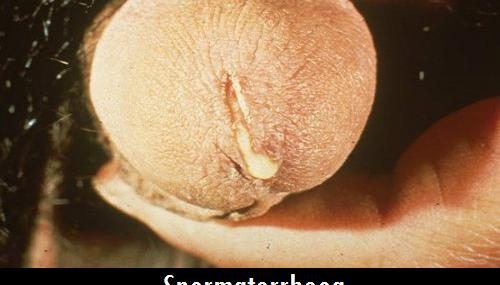
Spermatorrhoea (сперматорея) is a medical term used to describe a condition characterized by involuntary seminal discharge without ejaculation (orgasm) that occurs during urination.
Symptoms
What are the symptoms of Spermatorrhoea?
Main symptoms of Spermatorrhoea include:
The vast majority of patients describe the condition as constant or intermittent semen leakage without orgasm that occurs during urination, or during defecation due to strain.
Most patients complain about a thin milky or watery drop of clear, slightly sticky fluid at the meatus, which is extruded in greater quantity after urination or during defecation. Other common symptoms include:
- Meatus glued up in morning with a thick milky drop
- Urinary hesitancy, difficulty starting or maintaining urine stream
- Chronic straining when emptying the bowels
- Semen leakage during urination, semen comes out with urine
- Discharge of semen without ejaculation (orgasm) that occurs during urination.
Causes
What are the causes of Spermatorrhoea?
Noninflammatory Spermatorrhoea may occur spontaneously; However, in most cases, sexual perversion is believed to be the main cause of Spermatorrhoea. This includes self injurious behaviors and habits such as porn addiction, alcoholism, drug addiction, improper sexual behavior such as masturbating without orgasm for long, or achieving orgasm without ejaculation on long term, defying nature and practicing pervertism, anal objects insertion fisting, etc.
Other causes of Noninflammatory Spermatorrhoea include:
- Benign prostate enlargement (BPE, benign prostatic hyperplasia, BPH)
- Neuropathy due to diabetes mellitus
- Non infectious follicular prostatitis
- Sexual weakness due to strain
- Nerve Disorders, Spermatorrhoea can be caused by atony due to deteriorated nerve force from prolonged nerve compression.
- Zinc deficiency
- Sex addiction
- Compromised immune system
- B12 deficiency
- Malnutrition
If left untreated, noninflammatory spermatorrhoea may develop into follicular prostatitis.
Inflammatory Spermatorrhoea can be caused by:
- STD infections, such as gonorrhea, HIV, syphilis and chlamydia
- Gastrointestinal infections, such as E. coli, Shigella, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Clostridium, Rotaviruses, Giardia, Entamoeba, etc.
- Infectious follicular prostatitis
Diagnosis
How to diagnose Spermatorrhoea?
Diagnosis is based on symptoms and clinical findings
Laboratory tests can help identify anatomic abnormalities, determine a diagnosis, plan treatment, check to see if treatment is working, etc. These Lab tests can be used to help confirm diagnosis:
- CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis with iv contrast
- Urinalysis and culture to detect and identify microorganisms that may be causing a UTI
- A CBC blood test
- A digital rectal examination (DRE) is a simple test used to see if you might have an abnormal prostate. This test involves inserting a lubricated gloved finger into your rectum to palpate the prostate.
Treatment
How to treat Spermatorrhoea naturally?
Ginger tea is an outstanding herbal tea that is made from ginger root. Ginger is a medicinal herb, it has a long history of use for neurological and cardiovascular disorders, and for relieving digestive problems such as nausea, stomach cramps, loss of appetite, motion sickness and pain. This herb is considered optimal for the treatment of Spermatorrhoea.
Directions
How do you make fresh ginger tea?
- Wash, peel and grate the ginger root
- Place in 1 liter water
- Bring water to the boil
- Strain into a glass
- Add a few drops of lemon juice or lime. This step is optional
- Add sweetener of choice
- Serve. The tea is now ready to drink.
Drink two cups of ginger tea a day, one cup in the morning 20 minutes before eating breakfast, and another cup in the evening 30 minutes before going to bed.
Immunal® (Echinaceae purpurae herbae succus) is a herbal supplement used to enhance the immune system. Take one 80 mg tablet of Immunal® twice a day, after meals. Alternatively, add two 0.8 ml drops of Immunal® in 1/4 cup of water, take 3 cups a day, ideally before each main meal.[1][2]
Vitamin and Mineral Supplement (Vitamin C, Vitamin B12, Folic acid, Calcium, Magnesium, Zinc, etc.)
Etiotropic treatment
What medications can be used for Spermatorrhoea?
Antibiotics or antivirals to treat underlying infections
Prozac (fluoxetine) to treat anxiety, and stress
Trimedat (one 150 mg tablet, twice a day, before meals) and Ganaton (one 50 mg tablet 3 times a day, before meals) to treat IBS (irritable bowel syndrome) related symptoms.
Prevention
How to prevent Spermatorrhoea?
Lifestyle modifications, promoting healthy sexual lifestyle, having sex at least once a week, use condoms to prevent stds, get enough sleep, eat a balanced diet, stop porn addiction, stop using drugs, quit smoking cigarettes, drink plenty of fluids, get in shape, limit alcohol intake per day to no more than three servings (40.8 g)/day
Moderate alcohol consumption, regardless of beverage type, reduces risk of cardiovascular and neurological diseases.
Practicing sports, this should include at least 2 hours of physical workout per week
References
Verified by: Dr.Diab (October 1, 2020)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (October 1, 2020). What is Spermatorrhoea? Causes Symptoms and Treatment. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 27(2). urn:medcoi:article19165.













There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks