Malaria Causes Symptoms and Treatment
What is malaria and what is it caused by??
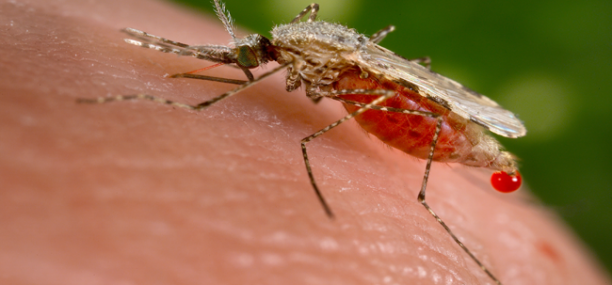
Malaria (малярия, الملاريا) is a mosquito-borne infectious disease caused by infection with one of four types of parasitic protozoans, a group of unicellular microorganisms in the genus Plasmodium, and transmitted by the bite of an infected mosquito. A single mosquito bite is all it takes to become infected.
Mosquito-bite diseases include Malaria, Dengue, Tularemia, West Nile virus, Zika virus, Chikungunya virus, Eastern equine encephalitis (EEE), Western equine encephalitis (WEE), Ross River fever, St. louis encephalitis (SLE), Yellow fever, etc.
Types
Malaria is caused by four types of parasitic protozoans:
- Plasmodium falciparum (tropical malaria)
- Plasmodium vivax ( 3 days malaria, pl. vivax)
- Plasmodium malaria (4 days malaria, pl. malariae)
- Plasmodium ovale (O ovale, pl. ovale)
Transmission
How can Malaria be transmitted?
Malaria is transmitted by the bite of an infected mosquito of the genus anopheles
Clinical picture
How long does it take for a person to get malaria?
The incubation period for three days malaria (Plasmodium vivax malaria) ranges from 1 to 3 weeks, whereas, the incubation period for tropical malaria (Plasmodium falciparum malaria) ranges from 8-16 days. The incubation period of Plasmodium malaria (four days malaria) ranges from 3-6 weeks.
The time from the initial infection until symptoms appear ranges from 1 to 3 weeks for Plasmodium ovale (P. ovale).
Symptoms
What are the early symptoms of malaria?
In most cases, symptoms of malaria usually occur between 1 to 6 weeks after the initial malaria infection. However, rarely, depending on the causative species (the type of plasmodium), it can take up to 6 months before any symptoms start to show
The four days malaria is characterized by an acute onset, symptoms usually develop abruptly and get worse overtime.
Triad of Symptoms
Shaking chills that can range from mild to severe, in malaria, chills are progressive in nature, this phase of malaria usually lasts about 1-3 hours, it is characterized by pale, cold, and moist skin, cyanosis, pain in the arms and flank pain
Fever and the feeling of heat, this phase usually lasts about 6-8 hours, fever rises, reaching 40-41 °c. Other symptoms alongside temperature include headache, hypotension, hallucinations, vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, hyperemia of the face and skin, dry skin, skin warm to touch
Excessive or profuse sweating (severe Perspiration), which is accompanied by an acute drop in temperature (hypothermia)
Symptoms repeat every 48 hrs for 3x days malaria, and every 72 hrs for 4x days malaria.
Other nonspecific symptoms include:
- Generalized malaise, weakness and myalgias (muscle pain)
- Icteric sclera and jaundice
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Severe depression, broken mood
What are the complications of tropical malaria?
Complications of tropical malaria include:
- Infectious toxic encephalopathy. Without prompt treatment, it can lead to malaric coma
- Infectious Toxic shock with hypothermia (algid malaria or malaric algid), it occurs in 0.4% of cases
- Acute kidney failure
- Acute pulmonary edema
- Hemoglobinuria
- Blackwater Fever, fever with black urine (or dark red urine)
Diagnosis
How to diagnose malaria?
- Thick blood smear
- CBC, characteristic laboratory features include signs of hemolytic anemia, and reticulocytosis
Treatment
How to treat malaria?
Malaria is usually treated with antimalarial drugs, such as Hydroxychloroquine, Chloroquine, and Quinine sulfate. Quinine (хинин, Chinin) is an antimalarial drug having antipyretic, analgesic, anti-smallpox and anti-inflammatory properties.
Quinine is usually given in combination with an antibiotic such as doxycycline, clindamycin, or tetracycline
What drugs are used to treat malaria?
The most common antimalarial drugs include:
Chloroquine (chloroquine phosphate, Aralen), an antimalarial drug used to treat malaria. Usual adult dose for malaria treatment is 2.5 g chloroquine phosphate (1.5 g base) in 3 days. An initial dose of 1 g (600 mg base) followed by an additional 500 mg (300 mg base) PO in 6 to 8 hours and a single dose of 500 mg (300 mg base) PO once daily for 2 days. Chloroquine is usually given in combination with primaquine, an antimalarial drug used in treating all cases of malaria.
Usual Adult Dose for Malaria Prophylaxis is 300mg base (500mg salt) per week starting at least 1 week before traveling to endemic areas. Individuals should take one dose of chloroquine per week while there, and for 4 consecutive weeks after coming back home.
Usual Pediatric Dose for malaria treatment is 5 mg/kg /week; however, dosage should not exceed the adult dose regardless of weight.
Quinine sulfate (Qualaquin), an antimalarial drug used to treat uncomplicated malaria. Usual adult dose for malaria treatment is 648 mg (542 mg base) orally 3 times a day for 7 days
Usual Pediatric Dose for malaria treatment is 10 mg sulfate salt/kg (8.3 mg base/kg) orally every 8 hours for 7 days; however, pediatric dose should not exceed the adult dose regardless of weight
Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil), an antimalarial drug used to treat malaria. Usual adult dose for malaria treatment is 2.0 g hydroxychloroquine (1550 mg base) in 3 days. An initial dose of 800 mg (620 mg base) followed by an additional 400 mg (310 mg base) PO in 6 to 8 hours and a single dose of 400 mg (310 mg base) PO once daily for 2 days.
Usual Adult Dose for Malaria Prophylaxis is 400 mg (310 mg base) per week starting at least 1 week before traveling to endemic areas. Individuals should take one dose of Hydroxychloroquine per week while there, and for 4 consecutive weeks after coming back home.
How to treat malaria naturally?
References
Verified by: Dr.Diab (December 13, 2017)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (December 13, 2017). What is Malaria? Causes Symptoms and Treatment. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 9(2). urn:medcoi:article15860.













One comment
Or use one of these social networks