Ovarian Cysts Causes Symptoms and Treatment
What is an ovarian cyst?
Ovarian cysts (ovarian cystadenomas, follicular cysts or corpus luteum cysts) are fluid-filled pockets or sacs that usually form during ovulation in an ovary or on its surface. In most cases, women with ovarian cysts are asymptomatic. However, when symptoms are present, they can include pelvic or lower abdominal pain, abdominal pressure or heaviness, bloating, and lower back pain.
Females have two ovaries, each ovary is a about the shape and size of an almond. Normally, the size of an ovary is about 3.5 cm in length, 1 cm thick, and 2 cm wide.
How long does it take for an ovarian cyst to go away?
Ovarian cysts are usually harmless, and in most cases, cysts resolve on their own in 1 to 3 months without treatment. However, In rare cases, ovarian cysts may rupture and the results could be life-threatening. Ruptured ovarian cysts, can cause acute sharp pain, and internal bleeding.
Acute sharp pain in the lower abdomen may indicate rupture, adnexal torsion, or hemorrhage.
Infrequently, ovarian cysts can rupture, leading to hemorrhage into the pelvis (internal bleeding into the pelvic cavity). This usually produces severe lower abdominal and pelvic pain that radiates to the back. A ruptured ovarian cyst can cause severe peritonitis (chemical peritonitis, or inflammation of the peritoneum).
Occasionally, ovarian cysts can rupture, leading to hemorrhage into the cyst or into the pelvis
Hemorrhagic ovarian cysts are one of the most common types of ovarian cysts that occur when a blood vessel in the cyst wall breaks and the blood leaks into the cyst, these cysts are commonly detected by physicians because hemorrhage into a cyst is usually painful (causing significant pain), forcing the patient to consult her doctor.
Alternatively, a cyst can rupture, releasing the cyst fluid into the abdominal cavity. This usually triggers a sudden onset of pain
In most cases, ovarian cysts usually form during ovulation, when the ovary releases an egg. However, there are many types of ovarian cysts, and they can occur during postmenopause, menopause, and pregnancy.
Can a cyst stop you from ovulating?
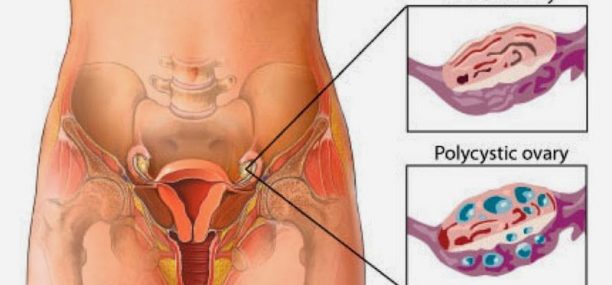
In most cases, ovarian cysts don’t affect fertility. However, women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) usually have difficulty in conceiving (fertility problems).
Symptoms
What are the symptoms of ovarian cysts and what does it feel like to have an ovarian cyst?
Ovarian cysts (follicular cysts) are usually asymptomatic; However, when symptoms are present, they can include:
- Acute sharp pelvic or lower abdominal pain, a dull or sharp pain on the side of the cyst
- Lower back pain
- Abdominal pressure or heaviness
- Bloating
- A pulling or sharp pain in the lower abdomen on either side of the uterus when a woman moves
What are the symptoms of ruptured ovarian cysts?
Symptoms of ruptured ovarian cysts include:
- Acute sharp lower abdominal pain
- Low grade fever
- Rebound tenderness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hemorrhagic shock
Cyst rupture may result in a severe life threatening peritonitis (infection and inflammation of the peritoneum).
Patients with ovarian torsion often present with acute onset crampy abdominal pain, usually unilateral lower abdominal pain
Causes
What causes ovarian cysts?
During the menstrual period, an ovarian egg grows in a follicle (a small sac). Normally, this sac breaks open, releasing the egg through the uterine tubes (oviducts) toward the uterus. However, if the follicle doesn’t break open, the ovarian follicle fills with fluid and causes a follicular cyst. Alternatively, If the cyst forms after the egg is released from the ovarian follicle it is called a corpus luteum cyst.
Ovarian torsion (adnexal torsion) is commonly associated with an underlying ovarian cyst, or tumor (mass). If you have an ovarian cyst in or on your ovary, it makes it more likely to develop ovarian torsion. Unrelieved ovarian torsion often leads to hemorrhagic infarction and can cause peritonitis
Treatment
How to treat ovarian cysts?
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil) or naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), are common medications used to treat Pain
- In ovarian torsion, an attempt can be made to untwist the pedicle to conserve fertility, if the viability of the ovary can be predicted preoperatively by contrast-enhanced color Doppler sonography (ultrasonography). Laparoscopy can be used for diagnosis and treatment. In prolonged ovarian torsion, removal of the effected ovary is recommended to reduce your risk of blood clots (thromboembolism) because prolonged ovarian torsion and loss of blood flow can lead to blood clot formation and necrosis
How do you relieve ovarian cyst pain?
Use heat, such as a heating pad, to relieve cramping. However, be careful not to burn yourself. Alternatively, you can use over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol), or NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil) or naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn)
What is the treatment for ruptured ovarian cysts?
- Hospitalization
- IV Pain Medications, such as Toradol (ketorolac) and Ofirmev (acetaminophen)
- fluid and blood transfusion therapy, to have fluids or blood replaced due to internal bleeding
- Rarely, a ruptured ovarian cyst may need surgery
Next steps management
How to diagnose ovarian cysts?
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Diagnostic laparoscopy
References
Verified by: Dr.Diab (December 19, 2017)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (December 19, 2017). Ovarian Cysts Causes Symptoms and Treatment. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 4(2). urn:medcoi:article15706.













There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks