Hiatal Hernia Types Symptoms Diagnosis and Treatment
What is a hiatal hernia?
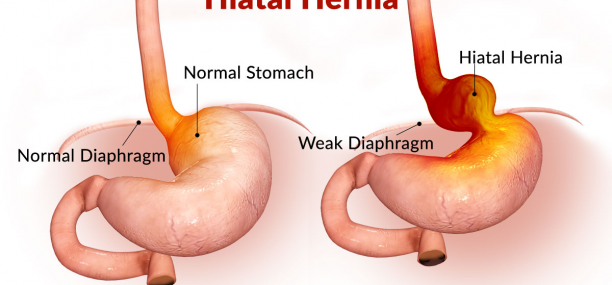
Hiatal hernia (грыжа пищеводного отверстия диафрагмы) is a medical term used to describe a condition in which the upper portion of the stomach (stomach cardia and fundus) protrudes into the chest cavity through the esophageal hiatus, which is a small opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus and the vagus nerve pass; however, in people with hiatal hernia, the esophageal hiatus can become dilated or enlarged allowing the positive abdominal pressure to push the stomach into the chest cavity. Most patients with Hiatal hernia suffer of acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux (GERD).
In normal healthy people, the esophageal hiatus is only large enough to accommodate the esophagus.
Types
1- Sliding hiatal hernia is the most common form of hiatus hernia where the hernia moves in and out of the chest.
2- Paraesophageal hernia (rolling hiatus hernia) is a rare and less common form of hiatus hernia.

What is hiatal hernia in the cardia?
The hiatus is an opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus and the vagus nerve pass.
The diaphragm is a muscular wall separating the abdominal cavity from the chest.
In patients with hiatal hernia or hiatus hernia the upper portion of the stomach ((stomach cardia) bulges up into the chest through dilated or enlarged esophageal hiatus.
What is the size of a hiatal hernia?
Hiatal hernias smaller than 2.5 inches (~6 cm) in size rarely cause symptoms. In most cases, smaller Hiatal hernias do not cause pain. However, very large hiatal hernias and paraesophageal hernias can cause a variety of symptoms such as gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), palpitations, heartburn, gastralgia and chest pain (upper abdominal pain). When symptoms occur, surgical repair of the hernia is mandatory to prevent strangulation of the stomach.
Where is a paraesophageal hernia located?
Paraesophageal Hernia (Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia) is a hiatal hernia in which part or all of the stomach herniates through the hiatus into the chest cavity or thorax whereas the esophageal hiatus remains in its normal location. Normally, the esophagus passes through the esophageal hiatus and attaches to the stomach.
Any time an organ pushes into an area where it doesn’t belong, it’s called a hernia.
Symptoms
What are the symptoms of a rolling hiatus hernia?
Common signs of paraesophageal hernia include:
- Heartburn and GERD
- Sudden chest pain that can’t be treated with antacid.
- Dysphagia or difficulty swallowing.
- Dyspnea or shortness of breath.
- Gastralgia or stomach pain.
- Indigestion.
- Nausea and Vomiting.
- Palpitations and dizziness due to vagus nerve irritation.
What are the symptoms of a sliding hiatus hernia?
Many patients with a sliding hiatus hernia are asymptomatic; however, others may present with any of the following symptoms:
- Heartburn a retrosternal or epigastric burning sensation that characteristically increases on bending or lying down.
- Gastro oesophageal reflux.
- Dyspnea or shortness of breath.
- Dysphagia or difficulty swallowing.
- Palpitations and dizziness due to vagus nerve irritation.
- Burping (belching) and bloating.
Is a hiatal hernia life threatening?
Hiatal hernias pose no threat to life and are rarely life threatening. Most cases of hiatal hernias are mild and cause few or no symptoms. However, complications of a hiatus hernia, such as incarcerated hernia or strangulation of part of the stomach poses a threat to life and can be life threatening if left untreated.
What causes a hiatal hernia?
Most cases of hiatal hernias are caused by diaphragm myopathy (a weakness of the diaphragm muscle) and most individuals with hiatal hernias are asymptomatic (have no symptoms). However, hiatal hernias often cause acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux (GERD).
Gastroesophageal reflux is when gastric juice (gastric acid or stomach acid) backs up into the esophagus.
How to diagnose a hiatal hernia?
Barium swallow x ray, a barium swallow is a procedure to examine the esophagus and upper GI tract to diagnose diseases such as hiatal hernia, dysphagia, peptic ulcer disease, etc. It involves swallowing a yogurt like meal that contains barium.
A barium swallow test takes about 15 minutes.
Endoscopy is a procedure where the esophagus and upper GI tract are examined using an endoscope.
How to treat a hiatal hernia?
Can you operate on a hiatal hernia?
Most individuals with hiatal hernias are asymptomatic; However, large hernias can cause symptoms such as acid reflux. Surgical therapy corrects these anatomical problems. The surgeon pulls the stomach back into the abdominal cavity, thus correcting the hiatal hernia.
The hiatal hernia causes no symptoms unless it is very large.
What is antireflux surgery?
If left untreated, hiatal hernias lead to chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which can cause complications such as esophagitis, esophageal ulcers, bleeding, or scarring of the esophagus. Laparoscopic antireflux surgery (also called Nissen fundoplication) is used in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease when medicines are not successful.
How do you repair a hiatal hernia?
This surgery involves repairing the hiatal hernia by:
- Pulling the stomach back into the abdominal cavity.
- Tightening the esophageal hiatus and the nearby diaphragm with stitches to keep your stomach from bulging upward through the hiatus hernia.
- Wrapping the upper part of your stomach around the end of your esophagus and fixing it with stitches.
How invasive is hernia surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery for hernia repair is a minimally-invasive surgical procedure that allows a surgeon to carry out surgical treatment without having to make large incisions in the skin, in this surgery the surgeon uses a laparoscope to fix a hernia while being guided by images projected and displayed on the LCD monitor.
A laparoscope is a thin tube with a micro video camera at its tip.
How long does it take to recover from a hernia?
After hernia repair surgery, most individuals are able to return to work after one or two weeks, although you may need prolonged postoperative care after hernia repair and more time off if your job involves manual labor.
Common postoperative tips after hernia repair surgery involve easy home exercises or gentle exercises. Gentle exercises such as walking can speedup the healing process; However, individuals should avoid intense training programs such as heavy lifting and other strenuous activities for about six to twelve weeks.
References
Verified by: Dr.Diab (October 8, 2020)
Citation: Dr.Diab. (October 8, 2020). Hiatal Hernia Types Symptoms Diagnosis and Treatment. Medcoi Journal of Medicine, 15(2). urn:medcoi:article17831.













There are no comments yet
Or use one of these social networks